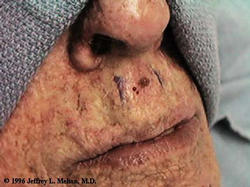
Skin Cancer Continued
Skin Cancer information continued
Risk Factors:
- Fair skin and red or blond hair
- Light-colored eyes
- Sunburning easily when exposed to the sun
- Having many moles, freckles or birthmarks
- Working or playing outside
- Being in the sun a lot as a child
- Having had a serious sunburn
- A family history of skin cancer
- Trying to get a tan in the sun or with a sunlamp
- Where a person lives - people who live in areas that get high levels of UV radiation are more likely to get skin cancer
- Lifetime exposure to UV radiation - most skin cancers appear after the age of 50, but the sun's damaging effects began at an early age
Diagnosis: Suspicious lumps, moles, or changes in the skin that persist for four to six weeks merit a visit to a physician for evaluation. At the office a biopsy (the surgical removal of tissue to determine the exact diagnosis) of the suspected growth may be done. The tissue is then examined under a microscope, and a diagnosis is made.
Prevention: Here are some preventive tips for reducing the risk of developing skin cancer:
- Avoid the sun during peak intensity (10:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m.)
- Wear sunglasses, a hat and tightly woven clothes when in the sun
- Don't use sun lamps or tanning booths
- Use sunscreen with a sun-protection factor (SPF) of 15 to 30
- Check skin every month to every three (3) months for signs of skin cancer